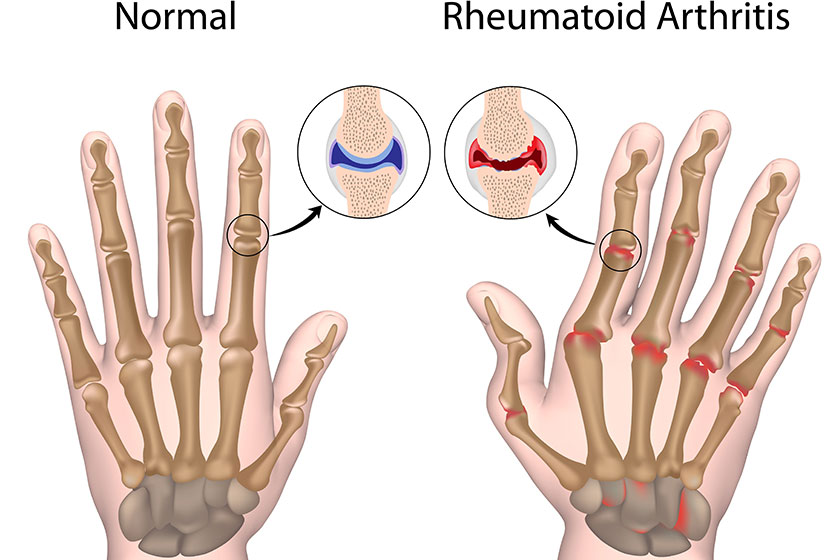
Rheumatoid arthritis, similar to Lupus, are autoimmune conditions that affect the body by mistakenly identifying parts of our body as invasive and damaging these tissues. Both diseases impair the immune system’s ability to distinguish between healthy and dangerous pathogens in the body, resulting in symptoms such as joint pain, fever, fatigue, and inflammation. While researchers are unaware of the causes of these autoimmune diseases, it is suspected that genetics, environmental factors, and hormones play a role in causing these diseases.
Rheumatoid arthritis vs lupus: how do these diseases differ, and how can we manage these diseases?
Symptoms
These two diseases can occur at any time in life. However, rheumatoid arthritis occurs more commonly in those between ages 35 and 50, and lupus is more commonly diagnosed in the young, with people of color being more commonly diagnosed with these diseases.
Both rheumatoid arthritis and lupus share general symptoms in joint pain and stiffness, swelling and inflammation, fatigue, and fever. However, symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis that are not experienced by those suffering from lupus include warmth near the swollen joints, rheumatoid nodules, and hand and foot deformities and dislocations. Lupus, however, has symptoms exclusive to it as well, such as rashes that develop into sores or lesions, hair loss, anemia, pain in the chest, and abnormal blood clotting, just to name a few.
Additionally, rheumatoid arthritis affects women three times more often than men.
Treatment
Neither of these diseases can be fully cured, with the goals of the treatment being the minimization of symptoms and the prevention of damage to the body, with long-term remission being the main goal of treatment. Both conditions are often treated by rheumatologists, who are specialized doctors dealing with musculoskeletal diseases and autoimmune conditions.
Drugs can be used to manage the symptoms of both diseases; most notably, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, and biologics are used. Certain antimalarial drugs can also be used in the treatment of these two diseases. Non-surgical treatments include physical therapy, steroid injections, massage therapy, and acupuncture just to name a few.
However, in the more severe cases of these diseases, certain surgical procedures are adopted to manage the symptoms, often as a last resort. With rheumatoid arthritis, joint replacement surgery is often used, with knee and hip replacements being the most common types of joint replacement surgery adopted. Surgical treatment for lupus differs from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, as doctors use dialysis or kidney transplants to help patients manage the disease.
Caring for Your Loved Ones at Morada Abilene
Rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are serious autoimmune diseases that should be properly managed, especially as we grow older and less equipped to handle their harmful symptoms.
Morada Abilene’s Assisted Living can provide your loved ones with the care and management of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Residents enjoy the benefits of assistance with daily living activities, regular housekeeping and maintenance, and a full calendar of activities. With three chef-prepared meals a day, complimentary transportation, and health and wellness programs also provided to every individual resident, you can rest assured that your loved ones will be well taken care of in our community. Feel free to contact us for further questions or to schedule a tour!